[email protected]
[email protected] No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China

+86-18158752211
 2025.12.08
2025.12.08 Industry News
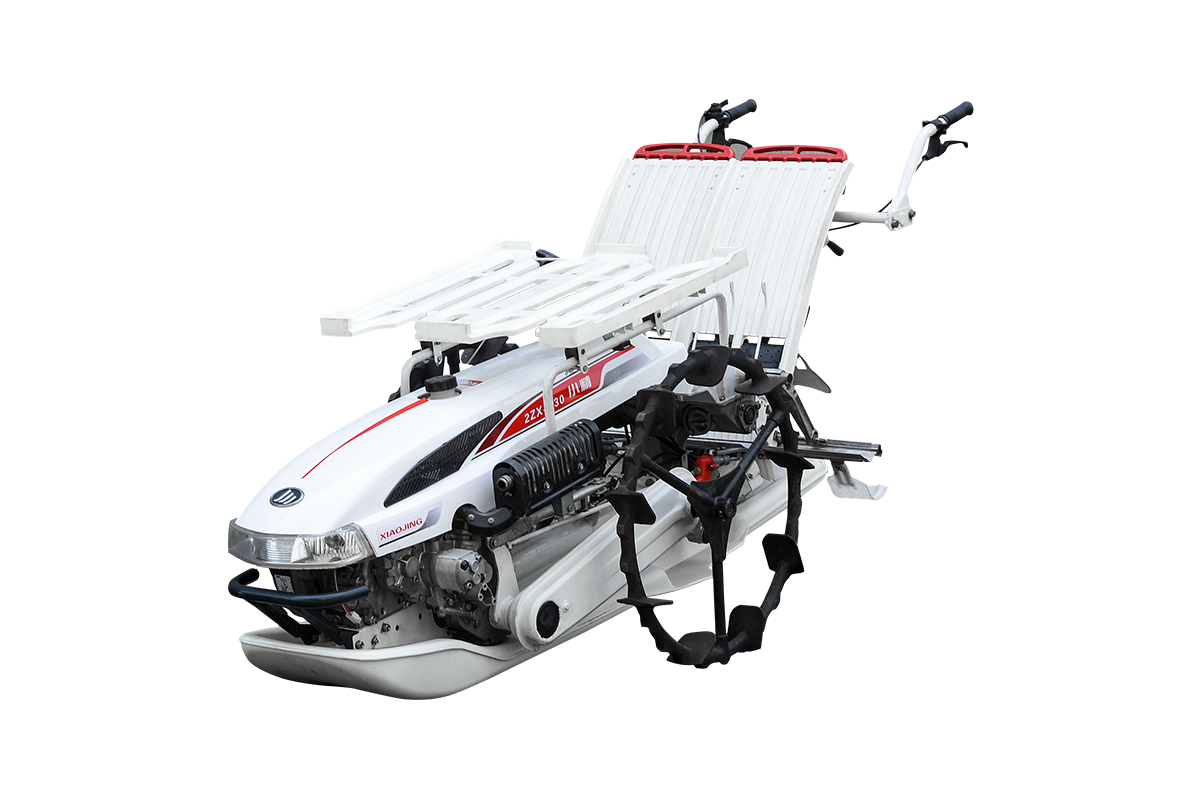
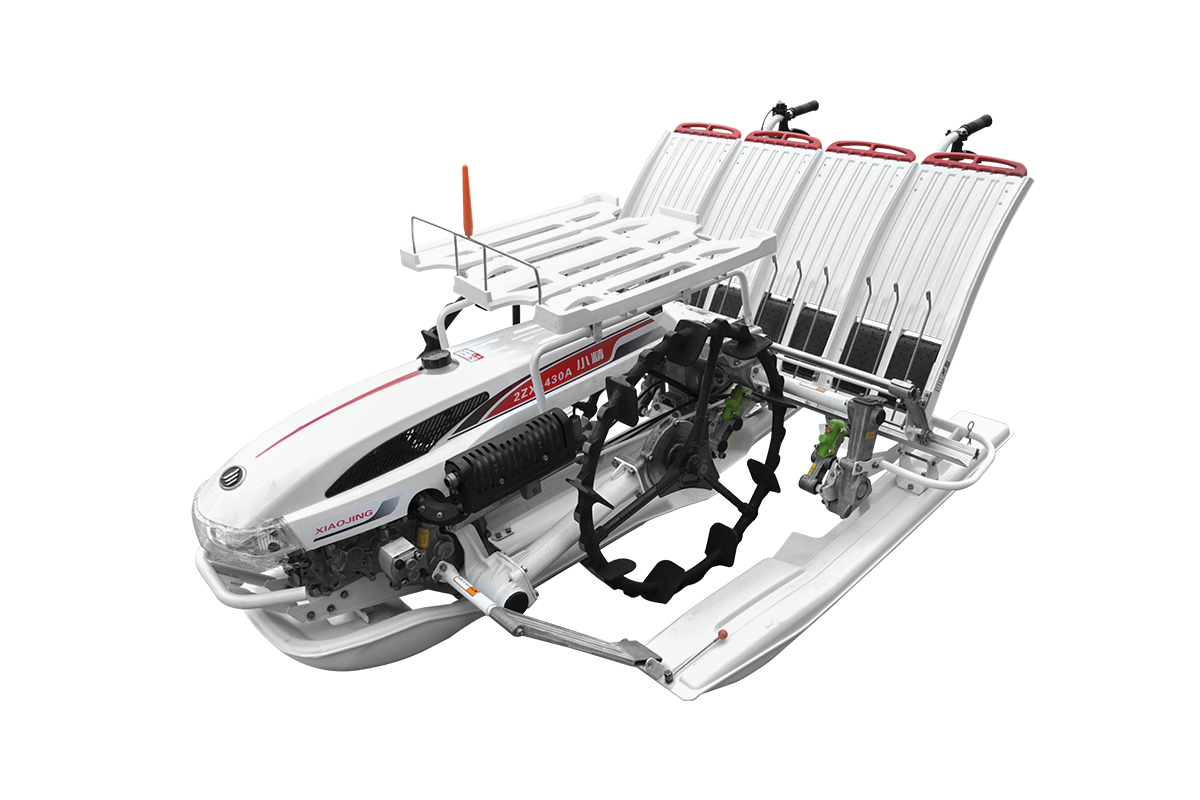
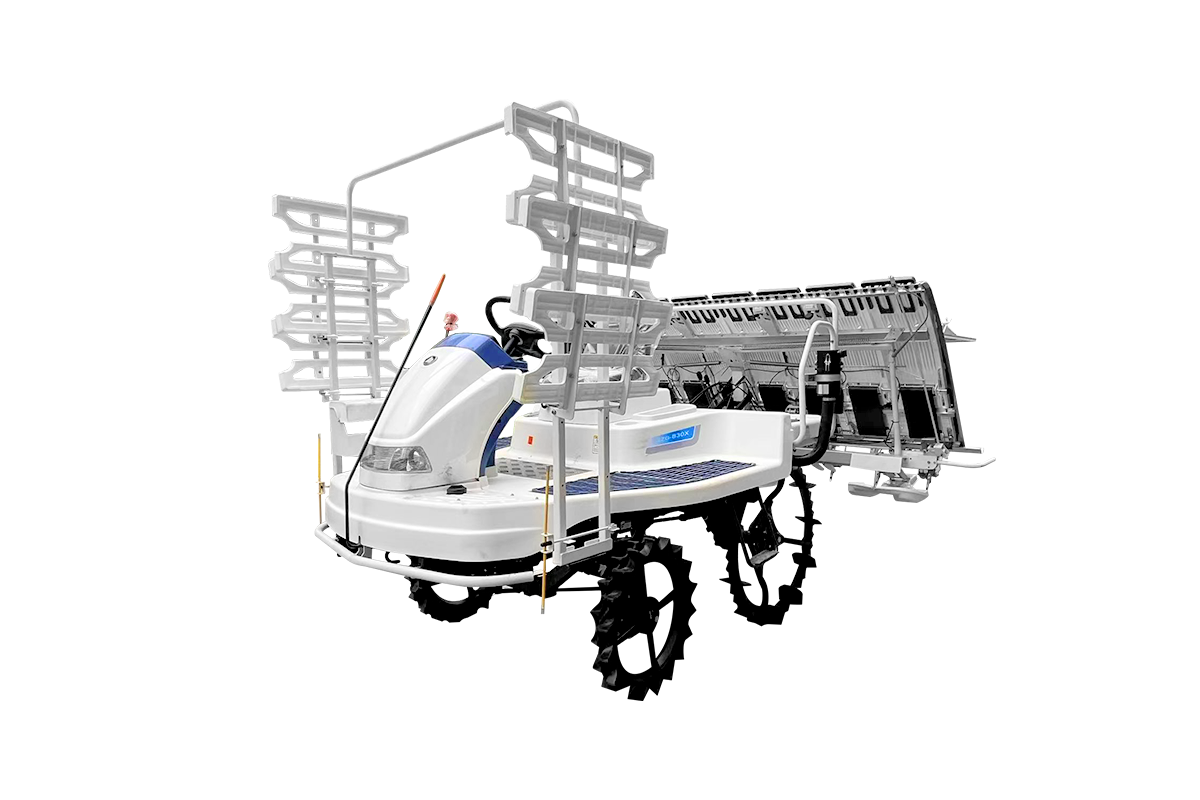
Industry NewsRiding type rice transplanters play a pivotal role in modern agricultural mechanization. The adjustability of track width is a crucial feature that enhances operational flexibility and efficiency. Rice fields differ in planting spacing across regions and cultivation practices. An adjustable track width design directly affects the machine’s adaptability and the quality of transplanting operations.
Track width refers to the horizontal distance between the two driving wheels of a rice transplanter. Proper track width ensures smooth movement in the field while preventing seedling damage or soil structure disruption. Narrow track width can cause the machine to sink into wet and soft soil, increasing operational resistance and reducing efficiency. Excessively wide track width increases turning radius, reduces maneuverability in the field, and can negatively impact uniformity and planting density.
Rice planting spacing varies depending on the variety, cultivation method, and local conditions. Common row spacing ranges from 20 cm to 35 cm. Traditional transplanters with fixed track width cannot meet diverse field requirements, limiting operational flexibility and farmer returns. Adjustable track width transplanters allow operators to modify the distance according to actual field conditions, ensuring that the wheels run between seedling rows. This prevents seedling compression or misaligned planting, ensuring high-quality transplanting.
Modern riding rice transplanters achieve adjustable track width through mechanical slides or hydraulic systems. Mechanical slide designs use bolt adjustments to manually set the desired track width. This method is simple and cost-effective. Hydraulic adjustment systems enable one-touch changes in track width, suitable for large or varied fields, enhancing operational efficiency and convenience. The design also considers wheel load-bearing capacity and structural strength to maintain stability after adjustment.
Adjustable track width affects not only machine mobility but also operational efficiency and rice growth. Proper track width allows smooth field movement, reducing wheel slippage and soil compaction. Well-maintained soil structure promotes seedling root development and nutrient uptake, increasing survival rate and final yield.
Adjustable track width enables a single machine to adapt to multiple planting spacings, reducing the need to purchase transplanters for each specific row spacing. In regions with intercropping or multiple rice varieties, adjustable track width significantly improves field operation flexibility and machine utilization. Farmers benefit from a higher return on investment, as one machine can handle diverse scenarios.
With the advancement of agricultural mechanization and smart technologies, adjustable track width systems are moving toward automation and digital control. Future transplanters may automatically detect field row spacing through sensors and adjust track width in real time, achieving precise operations. Integration with GPS and intelligent navigation systems will further improve accuracy, reduce seedling damage, and enhance overall production efficiency.