[email protected]
[email protected] No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China

+86-18158752211
 2025.09.29
2025.09.29 Industry News
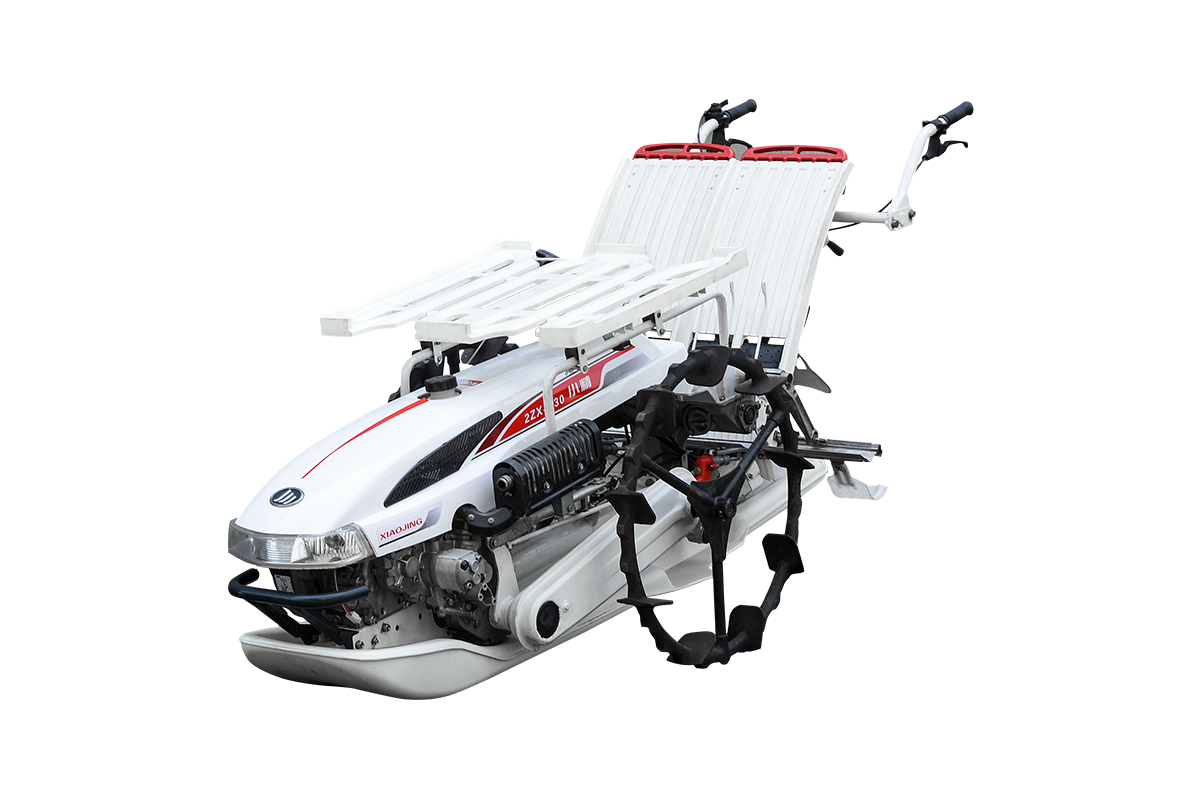
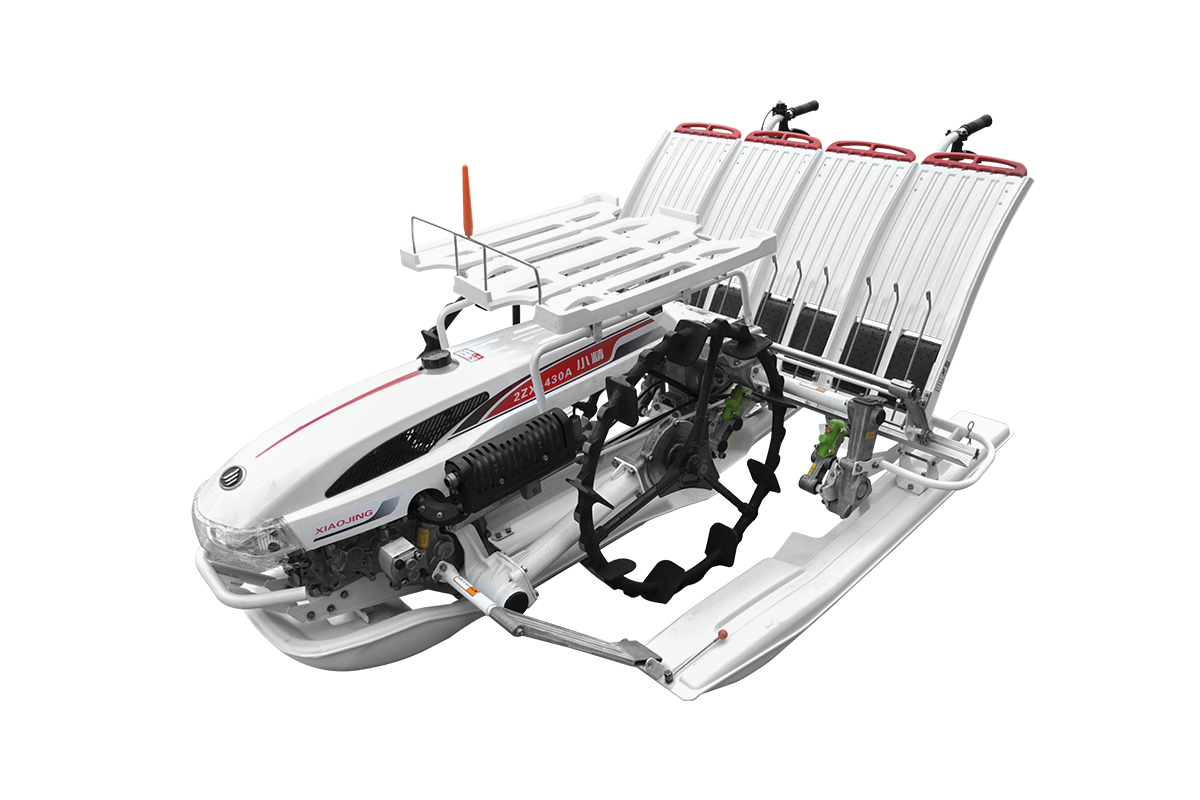
Industry NewsAs a core piece of equipment for efficient modern agricultural production, rice transplanters' operating performance and transplanting quality are constrained by multiple factors, with seedling quality being the key determinant of survival rate and operational efficiency. From a professional perspective, rice transplanters have strict and specific technical requirements for seedling tray specifications, seedling height, and root development. Meeting these requirements not only ensures continuous seedling supply and precise transplanting, but also significantly improves seedling survival rates in the field, ultimately reducing farm bounce rates and enhancing user trust in professional content.
Seedling Tray Specifications: The Technical Cornerstone of Standardization and Compatibility
The seedling tray specifications for rice transplanters are the primary prerequisite for ensuring smooth automatic seedling removal and continuous seedling delivery. These requirements involve the tray's dimensions, material rigidity, and hole structure.
1. Dimensional Compatibility
Mainstream rice transplanters, whether walk-behind or ride-on, use a specific Japanese (e.g., 60×30 cm) or national standard design for their seedling delivery platforms and guide rails.
Length and Width: The actual length and width of the seedling tray must strictly comply with the dimensional tolerances of the machine's seedling feed rails. Excessive length and width may cause the seedlings to become stuck, while too small may lead to unstable seedling placement, affecting seedling retrieval accuracy and causing missed or duplicate seedlings.
Thickness and Flatness: The bottom thickness and overall flatness of the seedling tray are crucial. Uneven seedling trays can easily warp or deform during vibration or feeding into the transplanting mechanism, affecting uniform seedling cutting, leading to root damage and uneven seedling harvesting.
2. Material and Rigidity Requirements
Seedling trays are typically made of plastic and must possess sufficient stiffness and toughness.
Stiffness: Insufficiently stiff seedling trays can easily deform during insertion or vibration, causing misalignment and compromising the robot's precise positioning.
Toughness: The material must withstand water immersion and sunlight exposure, resisting brittle cracking to ensure reusability and operational continuity. Professional equipment requires seedling trays to maintain geometric stability during the seedling removal and cutting process. Seedling Height: Compatibility of the Seedling Feeding and Planting Mechanisms
Seedling height is a key parameter that influences the coordinated operation of the seedling feeding mechanism and the transplanting arm of the rice transplanter. Improper height can cause a series of operational problems.
1. Suitable Height Range
Rice transplanters typically require the seedlings to be approximately 10 to 15 cm above ground level.
Seedlings Too High ("Tall Seedlings"): Seedlings that are too high are prone to lodging or becoming entangled during feeding, potentially blocking the seedling sorting comb or seedling feeding belt. During transplanting, the center of gravity of tall seedlings shifts upward, increasing the pulling force and friction on the seedlings by the transplanting arm, which can significantly increase the seedling damage rate and reduce wind resistance after transplanting.
Seedlings Too Low ("Short Seedlings"): Seedlings that are too low make it difficult for the robot arm to accurately grasp and cut the seedlings, resulting in missed plantings or insufficient individual seedlings, which reduces the number of effective ears. Furthermore, seedlings that are too low have less buoyancy in water, making them less likely to survive.
2. Seedling Uniformity
In addition to average height, the uniformity of individual seedling heights is equally important for transplanters. Excessive height variations will lead to inconsistent planting depths. Taller seedlings will be planted too deep, while shorter seedlings may float or become unstable, directly affecting the uniformity of seedlings in the field.
Root Development: Seedling Block Integrity and Damage Resistance
Root development directly determines the compactness and integrity of the seedling block, which is the fundamental guarantee for successful transplanter "pickup, delivery, and planting."
1. Root Interweaving and Compactness
Transplanters require that the seedling roots be fully interwoven to form a complete, solid seedling block.
Insufficient Root System: If the root system is sparse, the seedling block lacks cohesion. When the pusher claws or cutting blades on the transplanting arm are applied, the seedling block is prone to disintegration or shattering. A broken seedling block can cause seedlings to scatter, exposing their roots, leading to transplanting failure or seedling death due to dehydration.
Proper root packing: Ideally, the roots should form a dense network around the bottom and sides of the seedling tray. However, excessive clumping ("aging") is not recommended, as this increases resistance to mechanical cutting and may even damage the transplanting mechanism.
2. Seedling Separation Ease
The development of the root system also affects the seedling's **ease of separation**.
Removal Resistance: Seedlings with a well-formed root network maintain their integrity during robotic cutting and are removed from the tray with minimal shear and tensile resistance. This ensures a continuous supply of seedlings and a low seedling injury rate during high-speed operations.
Damage Resistance: Seedlings with healthy, white, and vigorous root systems are more tolerant and resilient to the compression, friction, and slight pulling caused by mechanical forces during transplanting, ensuring a high survival rate.