[email protected]
[email protected] No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China

+86-18158752211
 2025.09.22
2025.09.22 Industry News
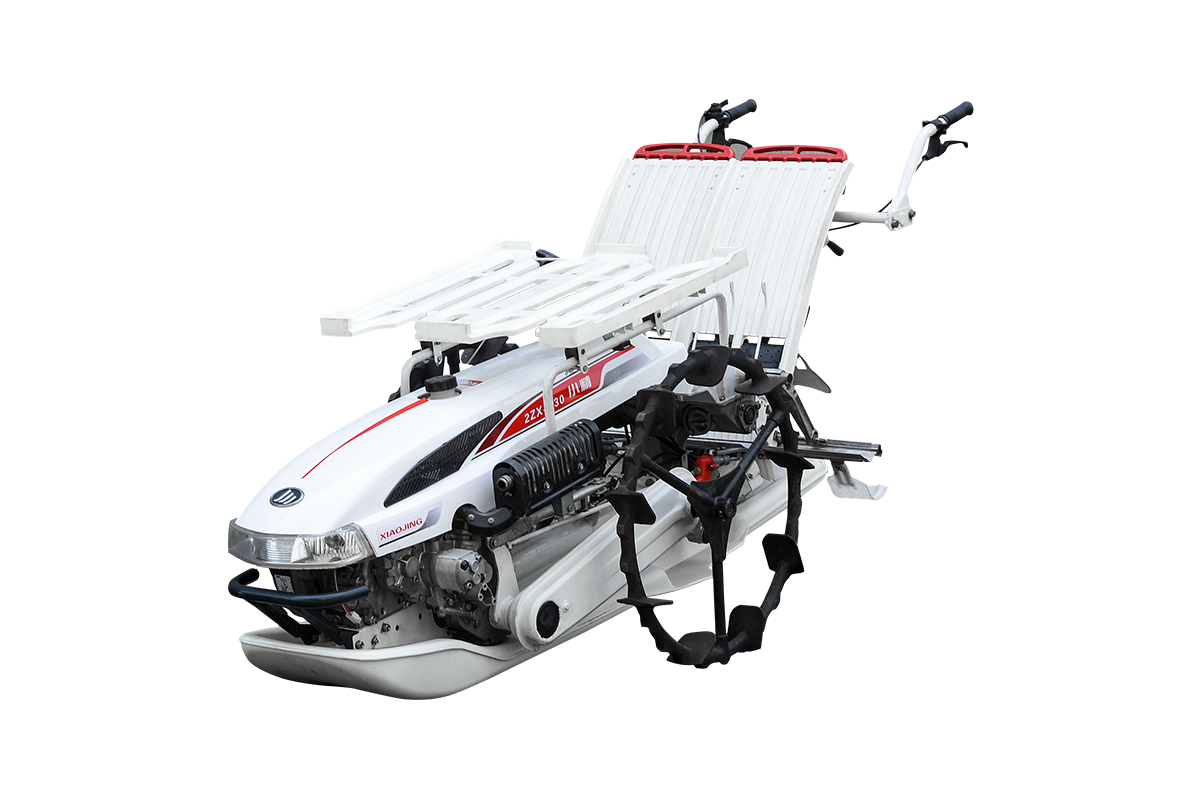
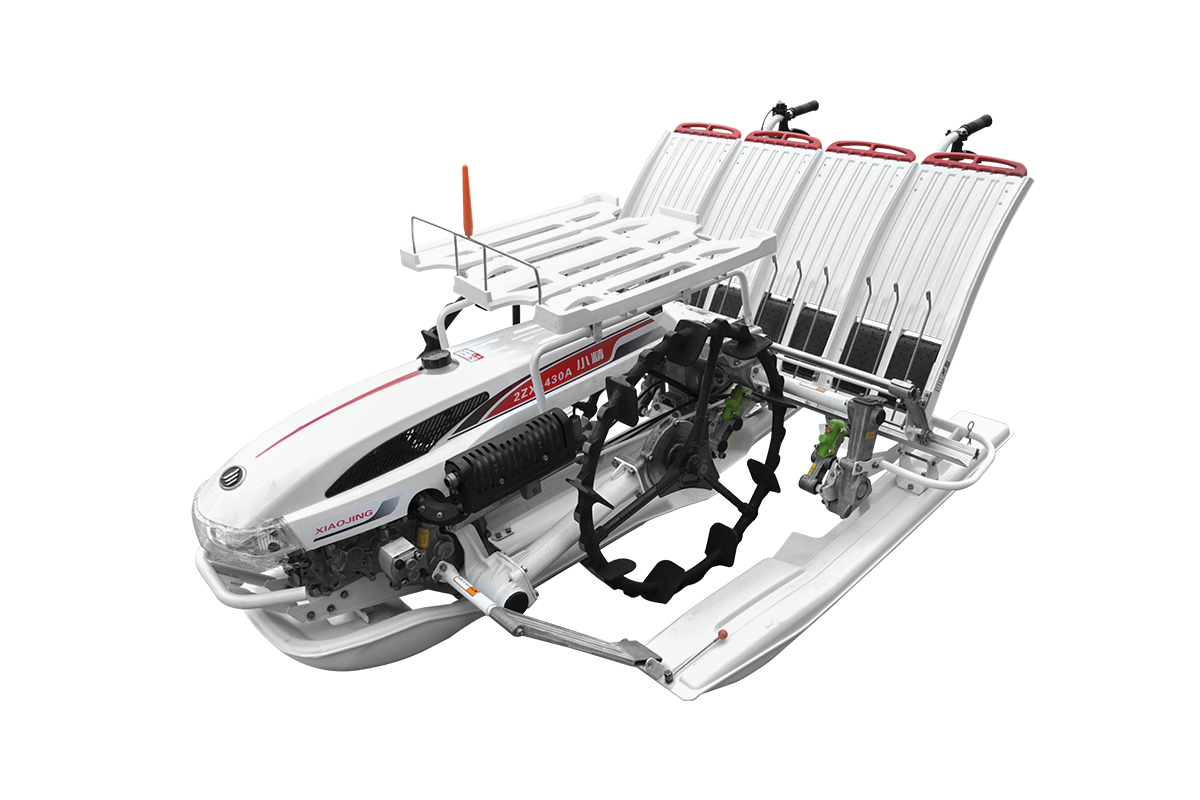
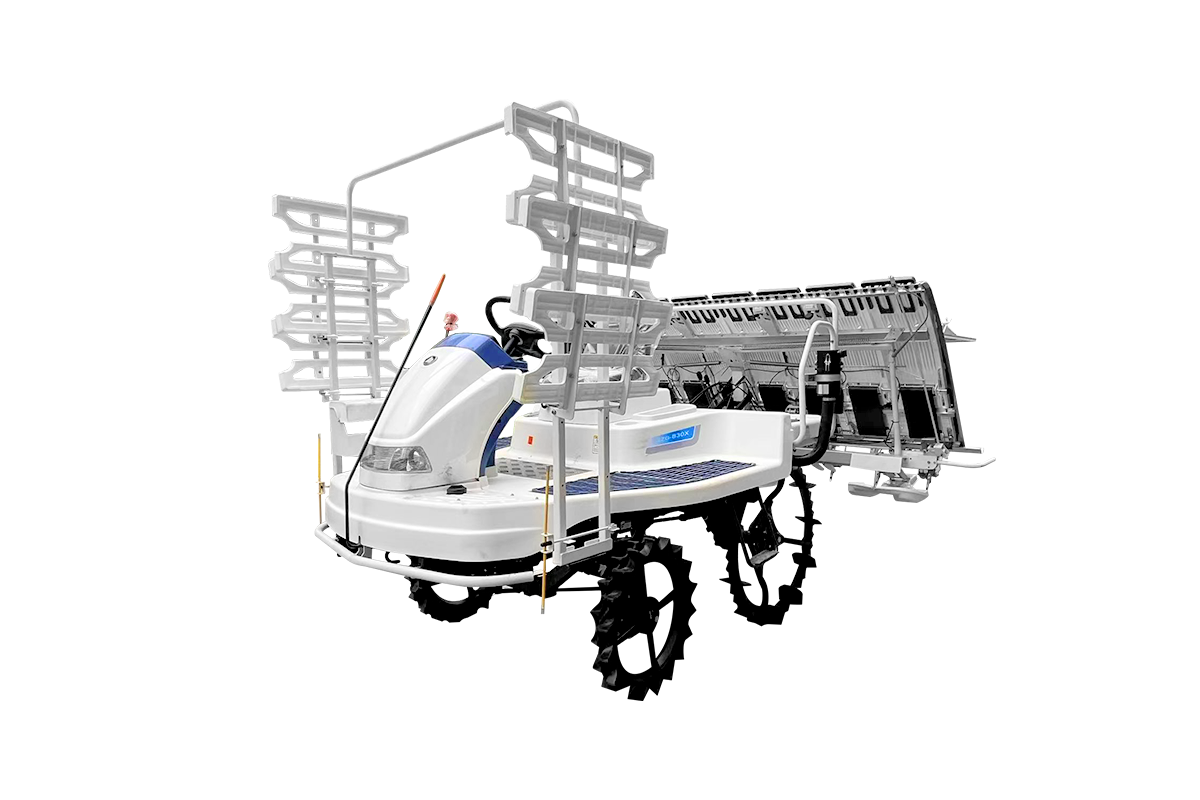
Industry NewsIn modern agriculture, vegetable transplanters are essential equipment for improving efficiency and ensuring yield. However, different vegetable varieties and seedling sizes vary significantly. From delicate lettuces to sturdy eggplants, their transplanting requirements are distinct. A high-quality transplanter must have flexible parameter adjustments to ensure perfect handling of different seedlings, high survival rates, and even field distribution. This customization capability is a hallmark of its expertise.
Adjusting Plant and Row Spacing: A "Precision Planner" for Crop Spacing
Plant and row spacing are key parameters that determine crop density in a field. Different vegetables have varying growth habits, leaf sizes, and light requirements, requiring varying planting spaces.
Transplanters adjust plant and row spacing by adjusting their mechanical structure. Row spacing is typically achieved by adjusting the position of the transplanting unit on the traction frame. For example, for vegetables requiring wide row spacing (such as broccoli and cabbage), the operator can manually or hydraulically move the transplanting unit outward to accommodate the larger growing space. Conversely, for leafy vegetables like lettuce and spinach, the transplanting units can be retracted to achieve denser planting.
Adjusting plant spacing requires more precision. This is primarily accomplished by controlling the frequency at which the seedling lifter drops seedlings. Transplanters are typically equipped with a chain drive or electronic control system. In chain drive systems, the spacing between seedlings can be adjusted by replacing sprockets with different tooth counts or adjusting the ratio of chain speed to overall machine speed. In more advanced electronic control systems, the operator simply enters the desired plant spacing on the control panel. The system, using a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and servo motors, precisely calculates and controls the movement of the seedling lifter, ensuring that each seedling lands in the desired position. This digital adjustment is both efficient and highly accurate.
Adapting to Seedling Size: The "Gentle Care" of the Seedling Lifter and Planting Depth
Vegetable seedlings vary greatly in size and shape. From seedlings with well-developed root systems like tomatoes and peppers to slender, fragile seedlings like celery and green onions, transplanters must be tailored to the needs of the seedlings.
Adjusting the seedling lifter is a key step. Common seedling extractors include air suction, clamping disc, and finger-type.
Air suction extractors use negative pressure to pull seedlings in the seedling tray and are suitable for loose, intact seedlings with intact root systems. To accommodate seedlings of varying sizes, you can change suction tips of different diameters or adjust the suction force.
Clamping disc and finger-type seedling extractors use mechanical gripping to grab seedlings. To accommodate the thickness of the seedling stems, you can adjust the size of the clamping disc opening and the gripping force. For example, for thick eggplant seedlings, you can increase the opening and gripping force; for slender onion seedlings, you need to reduce the opening and use less force to avoid damaging the seedlings.
Adjusting the planting depth is also crucial. Too deep will bury the seedling's growing point, while too shallow will expose the root system, affecting survival rate. Transplanters control the planting depth by adjusting the position of the furrow plow and covering wheel. Using an auger or hydraulic system, operators can precisely adjust the furrow depth and soil cover based on the seedling's root length and soil moisture. Some advanced models even feature automatic depth control sensors that detect ground elevation in real time and automatically adjust the coulter depth to ensure each seedling is planted at the optimal depth.
Coordinated Operation: Holistic Optimization of a Multifunctional System
An efficient transplanter is more than just a simple "catch and release" operation. It is a coordinated system encompassing multiple steps, including furrowing, fertilizing, watering, soil covering, and compaction. All of these functions need to be comprehensively optimized for different vegetable varieties.
For example, for leafy vegetables with high fertilizer requirements, strip fertilizer can be applied before or during transplanting, requiring adjustments to the fertilizer dispenser's output. For water-intensive fruits and vegetables, precise irrigation can be implemented immediately after transplanting, requiring adjustments to the water volume and spray coverage of the irrigation system. Adjustments to all these parameters must be precisely synchronized with the transplanting speed and seedling drop frequency to ensure a smooth and efficient operation.