[email protected]
[email protected] No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China

+86-18158752211
 2025.10.27
2025.10.27 Industry News
Industry NewsIn modern agricultural mechanization, rice seeders are key equipment for improving rice planting efficiency. Their power source directly impacts operational efficiency, operating costs, and scope of application. Rice seeders are primarily powered by diesel, gasoline, electric, and hydraulic power sources, each with distinct performance characteristics and applicable scenarios.
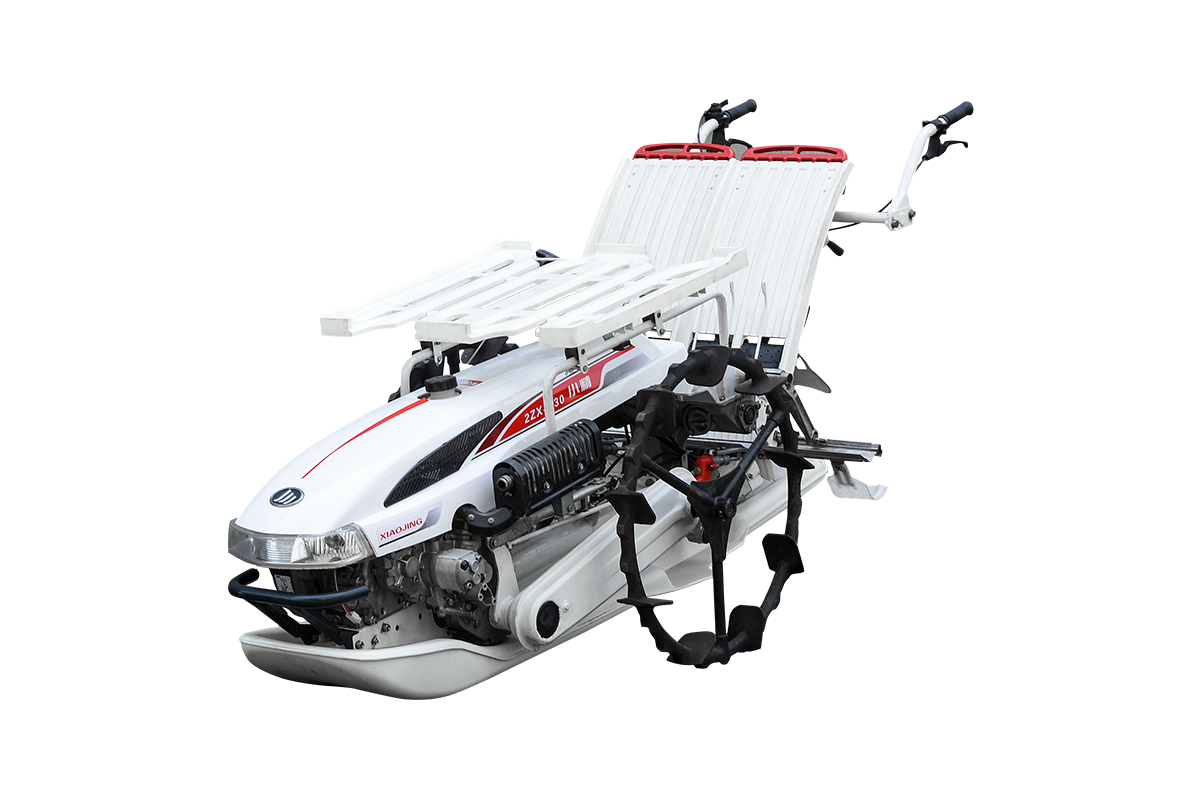
Diesel Power
Diesel power is the most widely used power source for rice seeders. Diesel engines offer high thermal efficiency and fuel economy, providing stable, high power output, making them suitable for large-scale paddy field operations. They maintain excellent torque output even at low speeds and high loads, ensuring reliable seeding in wet and soft soils.
The advantages of diesel power include relatively low fuel costs, sustained power, and high durability. They are suitable for long-term continuous operation and can support multi-row or wide-row spacing. Diesel engines are well-adapted to wet and muddy environments, with long maintenance cycles and no need for frequent part replacement.
The disadvantages of diesel power are high noise levels and relatively high emissions. Diesel engines are also relatively complex to start, and may experience difficulty starting in low winter temperatures. Furthermore, diesel-powered equipment is heavy and less portable, making it unsuitable for small farms or areas with complex terrain.
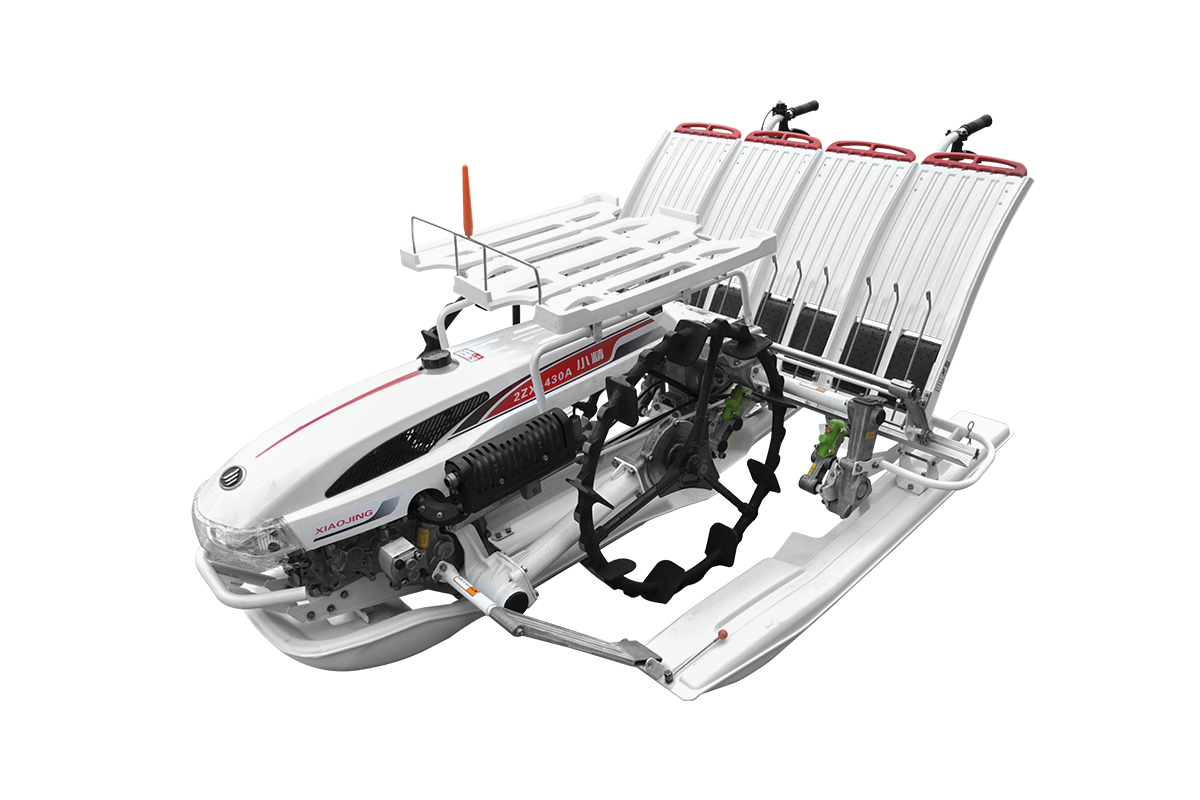
Gasoline-powered
Gasoline-powered rice seeders are primarily suitable for small or medium-sized operations. Gasoline engines start easily, run smoothly, and are quieter than diesel engines, providing a comfortable operating experience. Gasoline-powered equipment is generally lightweight, easy to transport, and maneuverable, making it suitable for small paddy fields or operations in complex terrain.
Gasoline-powered equipment has the advantages of ease of operation, relatively simple maintenance, and convenient fuel access. Its smooth engine operation and low vibration ensure a certain degree of seeding accuracy and uniformity. It is suitable for short, high-frequency seeding operations, allowing farmers to quickly complete field tasks.
Disadvantages of gasoline-powered equipment include higher fuel costs than diesel and a limited operating time limited by tank capacity. Gasoline engines are less efficient under high loads or when operating over large areas, and are prone to overheating. They are less adaptable to wet or muddy soils, resulting in relatively high maintenance costs over long periods of use.
Electric Power
Electric rice seeders use a motor to drive the seeding mechanism. With recent advances in battery technology, they have gradually entered the agricultural machinery market. Electric power boasts zero emissions, low noise, and a simple structure, making them suitable for agricultural production environments with stringent environmental requirements. Electric rice seeders are ready to use immediately, eliminating the need for warm-up time, making them easy to operate and requiring low maintenance.
Electric power offers advantages in environmental protection and energy conservation, making them suitable for operations near urban areas or in farmland subject to strict emission standards. Precise motor control enables intelligent adjustment of seeding depth and seed spacing, improving precision. The compact structure facilitates lightweight design and transportation.
The main disadvantage of electric power is limited battery life, with battery capacity directly determining operating time. Prolonged, high-load operation can lead to motor overheating and accelerated battery deterioration. Initial purchase costs are higher than those of traditional internal combustion engines, and battery replacement and maintenance require additional investment. However, they still have limitations for large-scale paddy field operations.
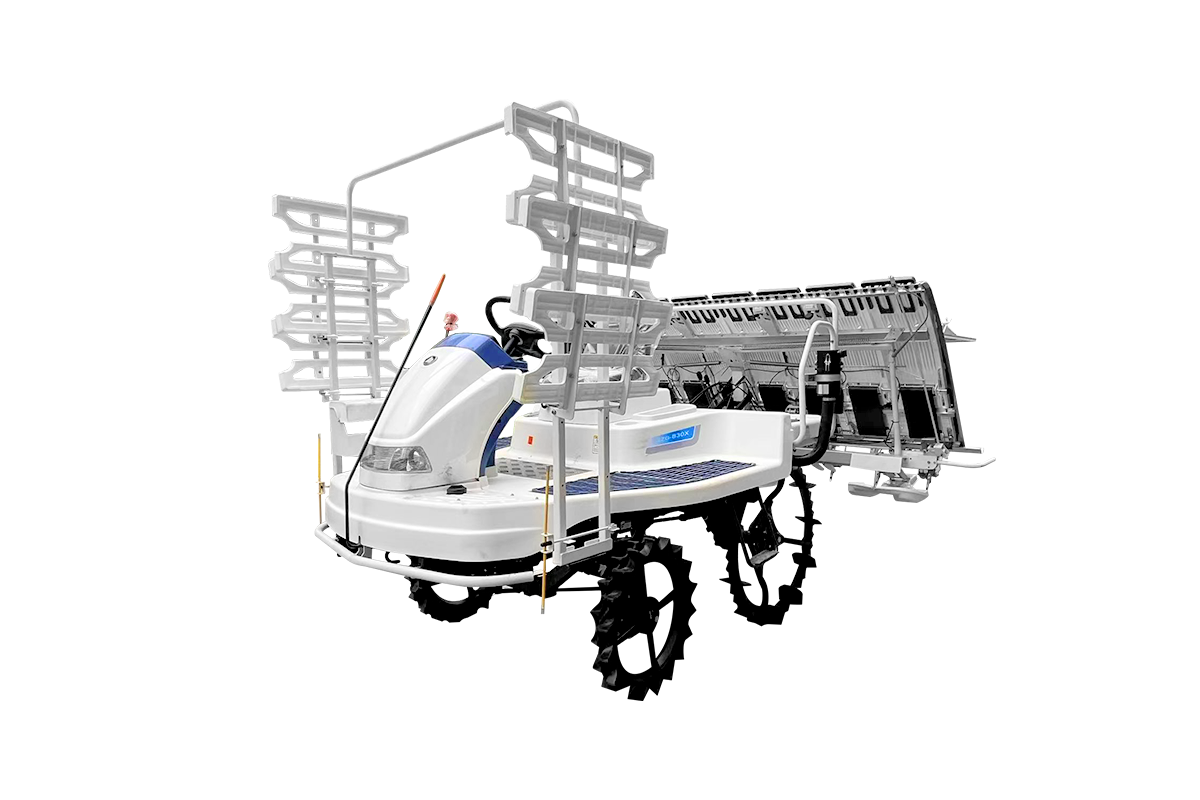
Hydraulic Power
Hydraulic rice seeders are powered by a hydraulic pump and are commonly used in large machinery or multi-purpose seeding equipment. Hydraulic power allows for precise control, smooth, and adjustable output, making them suitable for complex operations. The hydraulic system enables multi-functional attachment linkage, improving the planter's operational flexibility and automation.
The advantage of hydraulic power lies in its smooth power transmission, making it suitable for high-precision seeding operations. The hydraulic system can be combined with robotic arms, transplanting devices, and other equipment for automated operation, reducing manual intervention. It is suitable for large-scale farms and high-yield rice planting projects, improving overall operational efficiency and yield stability.
The disadvantages of hydraulic power include system complexity, high maintenance costs, and high operator skill requirements. Hydraulic oil leaks can cause environmental pollution, and equipment troubleshooting is complex. The overall equipment is heavy, and transportation and operation are restricted by terrain, resulting in high initial investment and maintenance costs.