[email protected]
[email protected] No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China

+86-18158752211
 2025.11.03
2025.11.03 Industry News
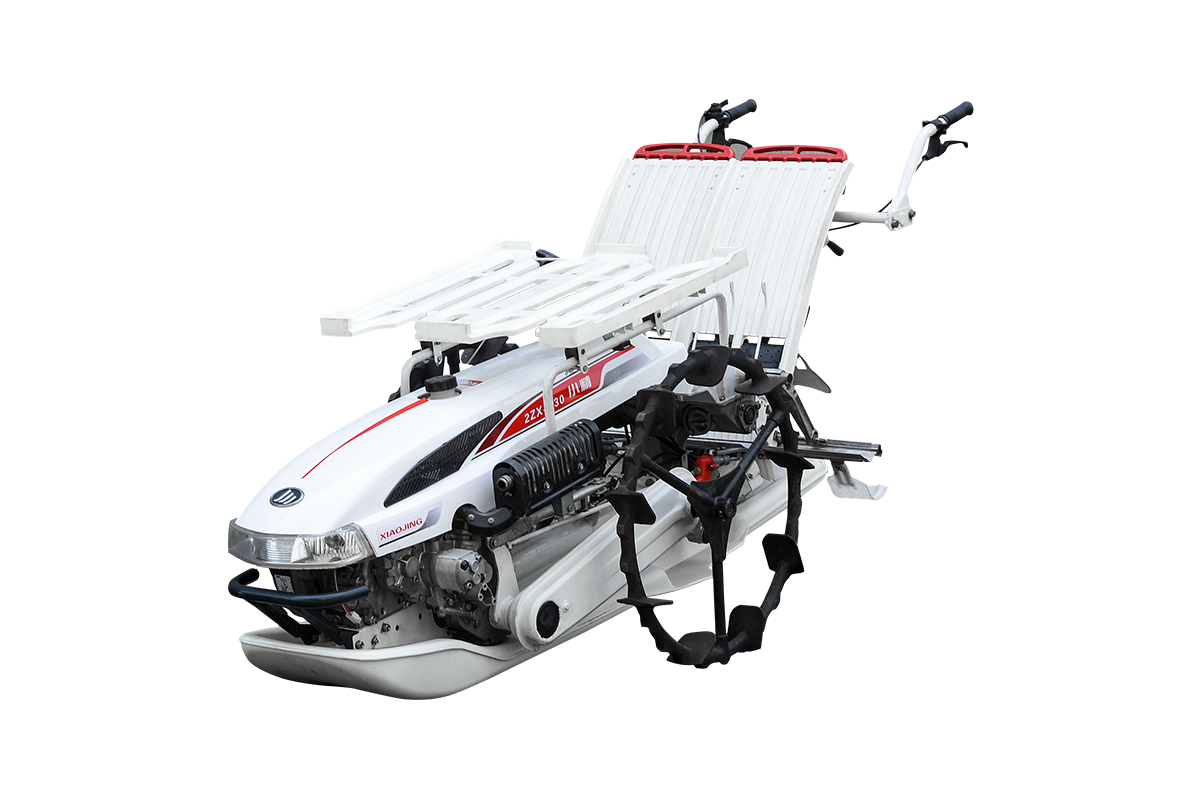
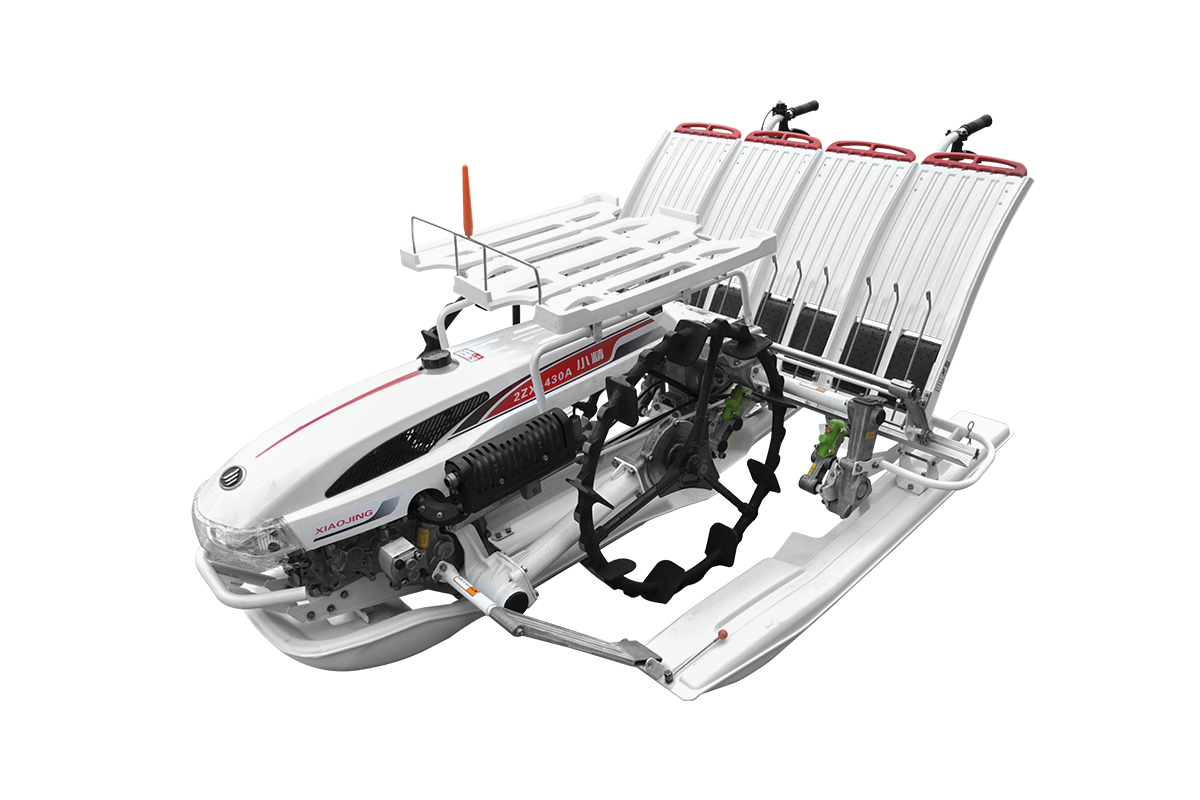
Industry NewsRice seeders play a vital role in mechanized rice production. Different climatic conditions significantly impact equipment performance, especially high and low temperatures. Ambient temperature not only affects the engine and powertrain, but also affects sowing accuracy, mechanical wear, and overall operating efficiency. Understanding the impact of temperature on rice seeder performance can help farmers and machine operators optimize operational schedules and equipment maintenance.
The Impact of High Temperature on Rice Seeders
High temperatures place a greater thermal load on the engine and powertrain of rice seeders. Diesel or gasoline engines are prone to overheating when operated at high temperatures for extended periods, resulting in reduced combustion efficiency and unstable power output. Hydraulic system oil viscosity decreases at high temperatures, potentially reducing hydraulic pump efficiency or increasing system leakage, affecting the smooth operation of the seeding mechanism.
High temperatures also affect the rice seeder's electronic control system. Temperature drift may occur in the electronic control module, sensors, and motor drive unit at high temperatures, leading to inaccurate control of sowing depth and seed spacing. The battery pack in an electric rice seeder experiences accelerated capacity loss at high temperatures, shortening its battery life and impacting the continuity of long-term operations.
High temperatures also accelerate the wear of mechanical components. Lubricant viscosity in seed dispensers, seeding wheels, and transmission gears decreases at high temperatures, increasing friction. Long-term operation can lead to premature wear of components. Plastic parts and rubber seals age faster at high temperatures, affecting equipment sealing and stability.
Operation accuracy is also affected by temperature. Soil moisture evaporates faster at high temperatures, creating a dry, hard soil layer that can reduce seeder penetration and uneven seed placement, impacting uniform rice seedling emergence. Mechanical vibration increases under high temperatures, potentially reducing seeding uniformity.
The Impact of Low Temperatures on Rice Seeders
Low temperatures also pose challenges for rice seeders. Diesel and gasoline engines have difficulty starting at low temperatures, and increased fuel viscosity leads to poor fuel injection and reduced power output. Hydraulic systems also experience increased oil viscosity at low temperatures, resulting in sluggish operation of hydraulic pumps and valves, slowing the response of the seeding mechanism and affecting operational efficiency.
Mechanical components are susceptible to damage in low temperatures. Thermal expansion and contraction of metal parts can cause gear meshing problems or bearing seizure. Plastic parts and rubber seals become brittle at low temperatures, prone to cracking or seal failure. Lubricants have poor low-temperature fluidity, increasing the risk of mechanical wear and failure.
Seeds sink less easily in cold soil. Rice seeders require more precise control of sowing depth, otherwise seeds may emerge from the soil surface, affecting germination rates. The battery capacity of electric rice seeders decreases significantly at low temperatures, reducing battery life and power output. This can lead to intermittent or even shutdown sowing.
Low temperatures also affect operator comfort and control sensitivity. The operating levers and control buttons become stiffer at low temperatures, making operation more difficult and challenging. Furthermore, soil moisture fluctuates significantly in low temperatures, increasing contact resistance between the seeding wheel and the ground. This can result in increased travel resistance and reduced operating speed.
Combined Impacts of High and Low Temperatures
The impacts of high and low temperatures on rice seeders primarily manifest in four areas: the power system, sowing accuracy, mechanical wear, and operating efficiency. Temperature fluctuations directly impact engine power and the stability of the hydraulic and electronic control systems. Seeding accuracy is affected by the seed distribution mechanism and soil conditions. Extremely high or low temperatures can lead to uneven seedling emergence. Extreme temperatures reduce the durability and lubricity of mechanical components, increasing maintenance requirements and the risk of failure. Operating efficiency decreases in extreme temperatures, increasing operating costs and impacting farmers' production plans.
The impact of temperature on rice seeder performance is closely related to the operating environment. When operating in large, hot fields or cold paddy fields, consider equipment load and operating intervals to optimize seeding schedules. Understanding the impact of high and low temperatures on equipment operation can help extend equipment life and improve seeding accuracy and efficiency.