[email protected]
[email protected] No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China

+86-18158752211
 2025.09.08
2025.09.08 Industry News
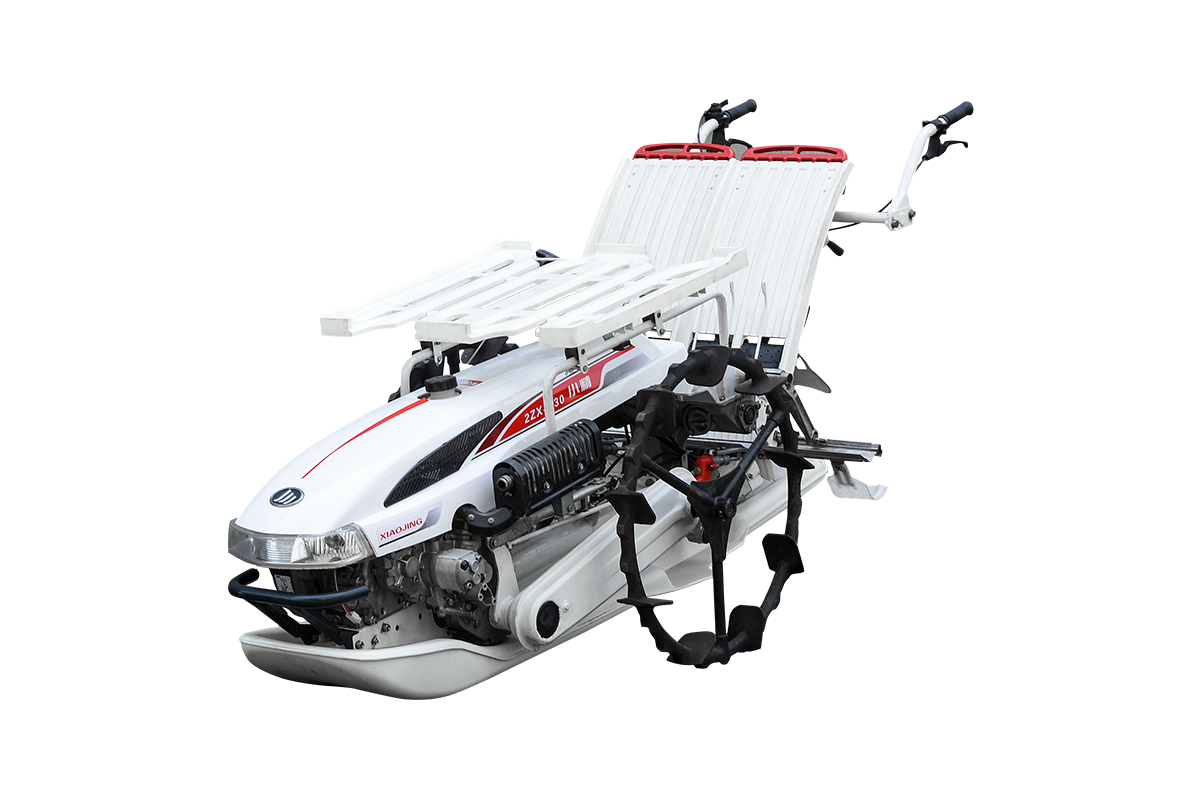
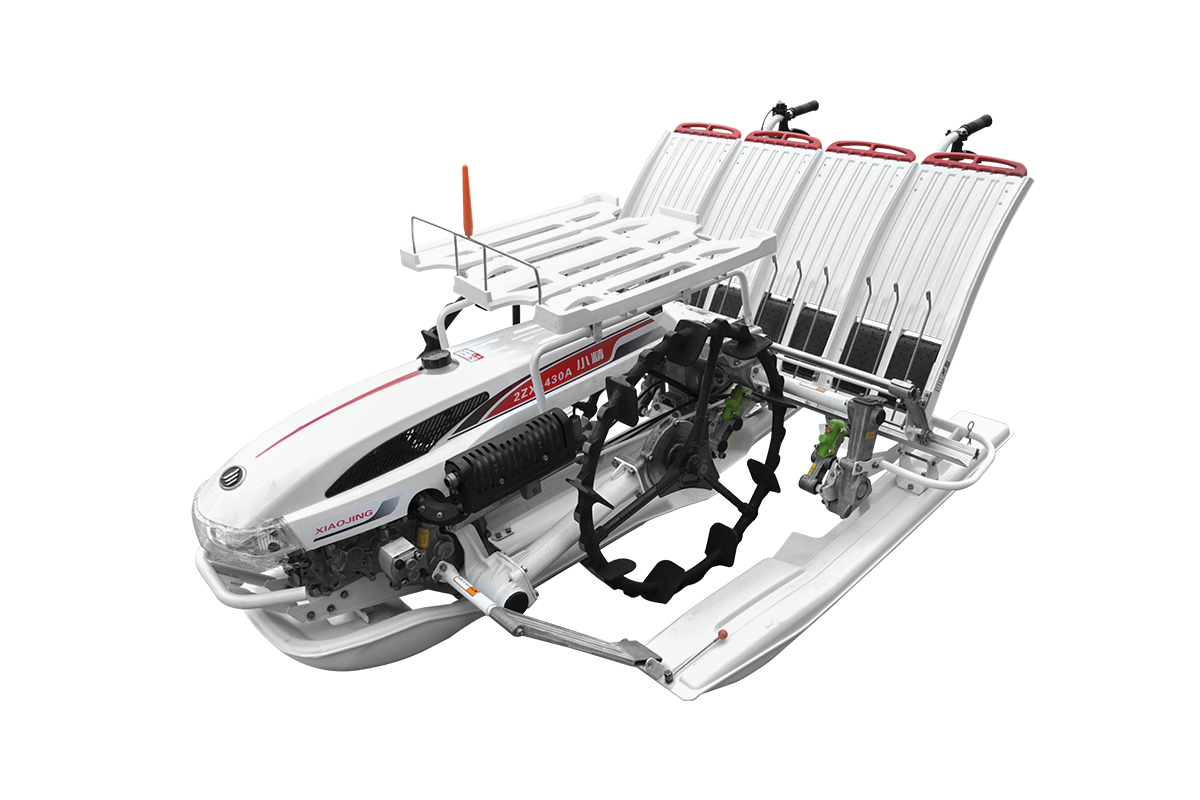
Industry NewsIn flat, well-groomed rice paddies, rice transplanter operation is relatively simple, focusing on maximizing efficiency and ensuring planting accuracy. This type of field provides an ideal working environment for rice transplanters, allowing them to fully utilize their advantages of high speed and large-scale operation.
For flat-land operations, the key requirements are maintaining straight travel and uniform planting. Operators should use markings on the machine or GPS/Beidou navigation systems to ensure that each row is aligned and avoid row spacing deviations. Furthermore, operators should maintain a steady throttle and a constant speed according to the set plant spacing and depth. The rice transplanter's float should be at optimal buoyancy to ensure consistent planting depth.
In this environment, rice transplanter failure rates are low. Key precautions focus on pre-operation preparation and routine inspections during operation. For example, check that the seedling trays are neatly arranged, that the seedlings are sufficiently moistened, and that the transplanting arms are free of foreign objects. During operation, regular inspections should be conducted to ensure planting quality. If any missed plantings or planting too shallowly or too deeply are detected, the machine should be stopped immediately for inspection and adjustments. Working on flat ground is the best environment to demonstrate the performance of a rice transplanter and is the preferred choice for technicians to conduct parameter adjustments and performance testing.
Muddy Rice Fields: Anti-sinking, Stability, and Precise Control
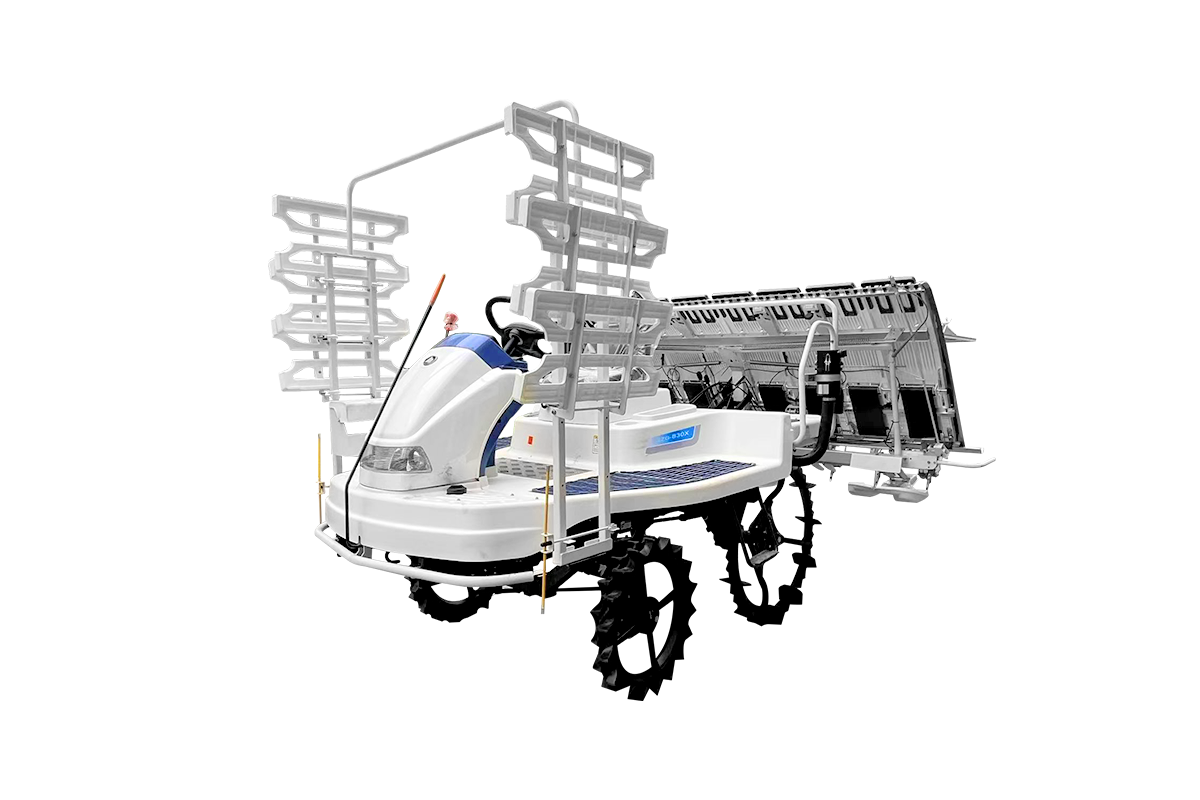
Unlike flat ground, muddy rice fields present multiple challenges for rice transplanters. Deep mud and poor soil bearing capacity can easily cause the machine to get stuck, impacting operational continuity and safety. In such conditions, special operating requirements and precautions increase significantly.
First, anti-sinking is paramount. Rice transplanters are typically designed with large-diameter, wide-width drive wheels to increase contact area and reduce ground pressure. Operators should avoid sudden acceleration or sharp turns in areas with particularly deep mud and maintain a steady and steady speed. Before entering muddy terrain, reduce speed appropriately to allow the machine to pass slowly and steadily. If the machine gets stuck, avoid blindly increasing the throttle; use tools or external force to slowly pull the machine out.
Second, maintaining machine stability is crucial. Muddy ground can cause the machine to shake, directly affecting planting depth and uniform plant spacing. Operators need to master the machine's direction and speed to minimize sway. Some high-end rice transplanters are equipped with automatic balancing systems, which automatically adjust the machine's position through hydraulic or mechanical means to ensure the planting mechanism remains perpendicular to the water surface, thus ensuring high-quality planting.
Slopes and Terraces: Balance, Steering, and Safety First
Slopes and terraces are the most challenging environments for rice transplanter operation. The uneven ground, narrow ridges, and height differences place high demands on the machine's maneuverability and the operator's skills.
Maintaining machine balance is crucial when operating on slopes. Sloping ground can shift the transplanter's center of gravity, affecting planting depth. Operators need to master the machine's balance control or rely on the machine's automatic balancing system to ensure the planting mechanism remains level. When operating up or down slopes, drive slowly to avoid excessive speed that could cause the machine to lose control.
Steering is crucial when operating on terraces. Terraced fields are typically small and irregularly shaped, with frequent turns at the headland. The operator must precisely control the direction and utilize tight steering techniques to avoid contact with the ridges. Furthermore, the timing of raising and lowering the planting mechanism on the ridge must be carefully controlled to prevent empty plantings or planting seedlings onto the ridge. Some machines have an automatic lift function at the edge of the field, which greatly simplifies this operation.
Furthermore, safety is paramount when operating on slopes and terraces. The risk of machine tipping increases due to complex terrain. Operators should always be aware of their surroundings and avoid operating on steep slopes. Before operating, carefully check the machine's braking and steering systems to ensure they are in good working order.