[email protected]
[email protected] No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 1819, Renmin West Road, Cao'e Street, Shangyu District, Shaoxing City, Zhejiang Province, China

+86-18158752211
 2025.08.25
2025.08.25 Industry News
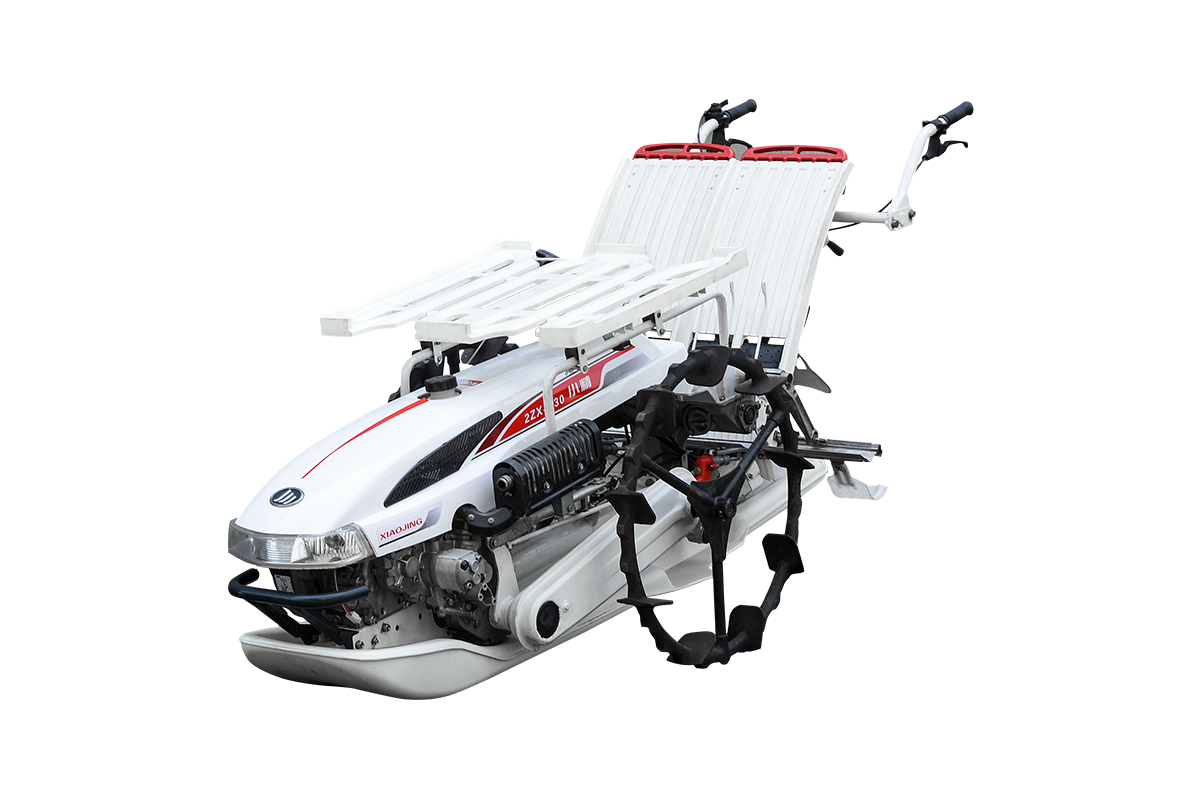
Industry NewsManual Transplanter Operational Characteristics
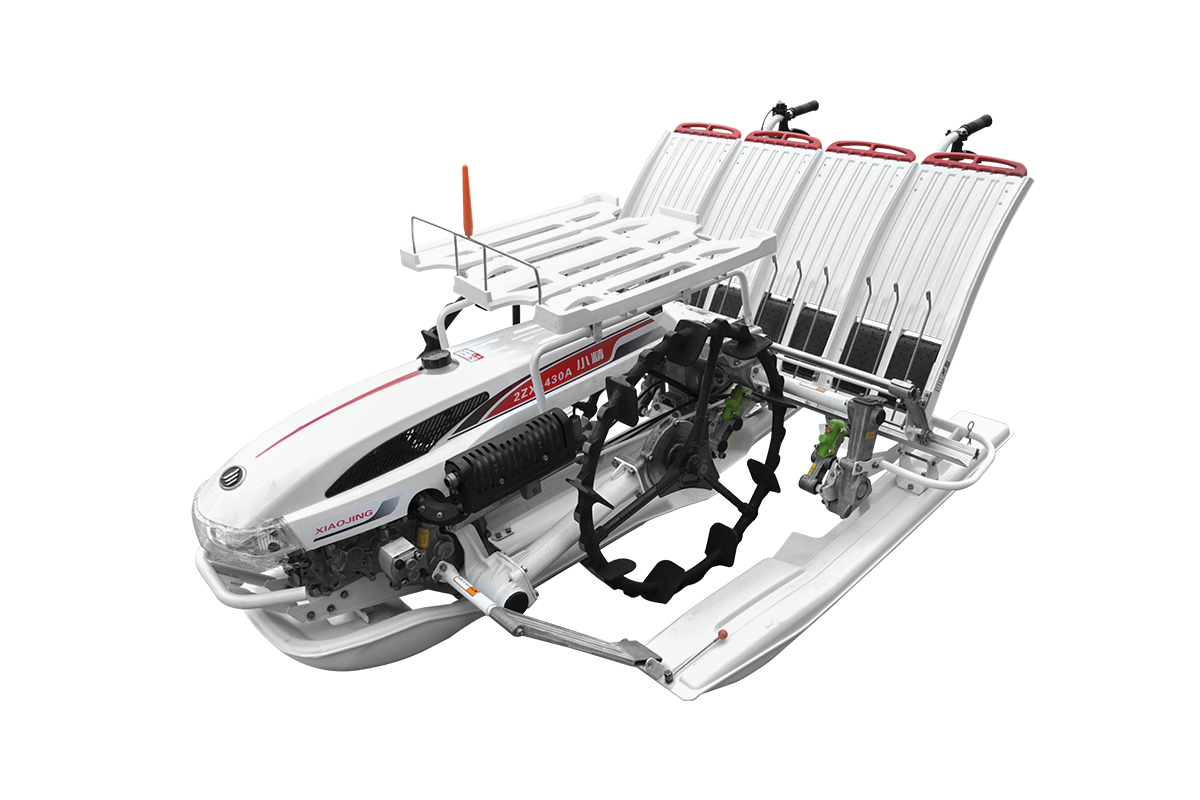
A manual transplanter is a mechanical device that relies on manual pushing or pulling to transplant seedlings. During operation, the operator must maintain a certain posture while controlling the machine's forward speed and planting depth to ensure uniform transplanting. These actions primarily include pushing forward, straightening, adjusting the push rod, and digging trench depth. While the mechanical design reduces the labor intensity of traditional manual transplanting, operation still requires continuous physical exertion.
The Impact of Operating Posture on Physical Exertion
When operating a manual transplanter, the operator typically pushes the machine in a half-squatting or forward-leaning position, which places prolonged tension in the shoulder, arm, and back muscles. Improper posture increases local muscle strain, leading to soreness and fatigue over a short period of time. After several hours of continuous operation, significant fatigue accumulates in the back and lower limb muscles, compromising operational accuracy. The handle height and wheelbase of a manual transplanter significantly influence operating posture. While appropriate adjustments can alleviate some muscle strain, they cannot completely eliminate physical exertion.
The Relationship between Propulsion Force and Operating Resistance
A manual transplanter's forward motion relies on the operator's thrust. Soil resistance, moisture, field flatness, and trench depth all affect the required pushing force. In clay or moist soils, pushing force requirements are significantly increased, requiring more physical effort to maintain speed. Prolonged operation can easily lead to general fatigue. In sandy or soft soils, resistance is lower, but frequent adjustments to the hole depth still require continuous force, leading to significant cumulative fatigue.
Operation Pace and Continuous Work
The operating pace of a manual transplanter is directly related to physical exertion and fatigue. While high-speed operation improves transplanting efficiency, it increases heart rate and muscle tension, accelerating physical exertion. While low-speed operation is relatively easy, maintaining the same posture for extended periods can still cause localized fatigue. Continuous operation over a certain period can lead to decreased precision, inconsistent hole depth, and increased seedling damage, indicating that physical exertion directly impacts work quality.
Psychological Factors and Fatigue
Physical exertion is not only determined by muscle load but also influenced by psychological factors. Operating a manual transplanter requires intense concentration to ensure accurate placement of each seedling. During continuous operation, sustained attention strain increases subjective fatigue, causing operators to tire more quickly. The combined effects of mental and muscle fatigue reduce work efficiency and increase operational risks.
Physiological Manifestations of Physical Exhaustion
Long-term operation of a manual transplanter can lead to elevated heart rate, increased breathing, and lactic acid accumulation in the muscles. This can cause soreness in the upper limbs, shoulders, back, and lower limbs, and operators may experience lower back stiffness and knee discomfort. Physical exertion varies significantly between operators based on gender, age, and physical condition. Younger operators have greater physical strength, but this may not necessarily translate to optimal operating efficiency. Older operators have limited physical strength, but experience can help them optimize their movements and reduce fatigue.
Design Factors That Reduce Physical Exhaustion
The mechanical design of a manual transplanter significantly influences physical exertion and fatigue. Proper design of handle height, wheelbase, push rod travel, and trenching resistance can reduce muscle strain and improve operator comfort. Some models incorporate support or guide wheels to reduce thrust requirements. Excessive overall weight or small wheel diameters increase operating resistance and accelerate physical exhaustion.